
According to a recent study that analyzed the early months of the Ukrainian war through a logistical lens, inadequate preparation, poor logistics, and unrealistic planning are among the factors that led to the failure of Russia’s swift invasion of Ukraine.
MILITARY LOGISTICS: WESTERN LOGISTICS PRINCIPLES
The logistical planning at the operational level involves prioritizing and distributing resources to logistics hubs, which are then transferred to tactical logistics units to support combat units. The goal is to ensure that the right supplies are delivered to the right place and person at the right time, in the right quantity and condition. In military operations, logistical support can be provided in three ways: military units can bring supplies with them, logistics units can establish supply lines from safe areas to the combat units, or the deployed units can obtain resources from the local area. The logistics planning must take into account the demands forecasted in the operational plan or the actual demands from the fighting units. The availability of supplies depends on various factors such as safety, environment, weight or volume, risk, longevity, durability, and procurement principles. The logistics planning must also consider the four Ds: the demand, distance, destination, and duration of a specific demand.
MILITARY LOGISTICS: RUSSIAN LOGISTICS PRINCIPLES
In the Soviet era, the offensive operations concept was based on the “echelon principle,” which involved replacing exhausted echelons with fresh ones. This principle depended on army groups supported by Material Technical Support brigades, and the main means of transportation were railways and pipelines. However, modern Russia lacks the capability to mobilize and sustain a multi-echelon force for a prolonged war. After a major transformation in 2009, Russia modernized its operational concept and replaced the Soviet logistics system with a leaner one involving downsizing and outsourcing, which was largely untested in combat operations. Military planning in Russia follows a strict hierarchical, top-down structure, with the Force Commander choosing the course of action and the commander’s staff detailing how to proceed. The logistics planning follows predefined principles, well-exercised scenarios, and calculations of ammunition consumption and attrition. Logistics on the army group and brigade levels are standardized and largely follow the same principles as they did in the Soviet era. However, a recent assessment of the future development of Russian military capability asserts that the main restriction of the Russian Armed Forces will not be availability of forces, but logistics.
ZAPAD-2021: PLANNING AND PREPARING LOGISTICS FOR
A WAR?
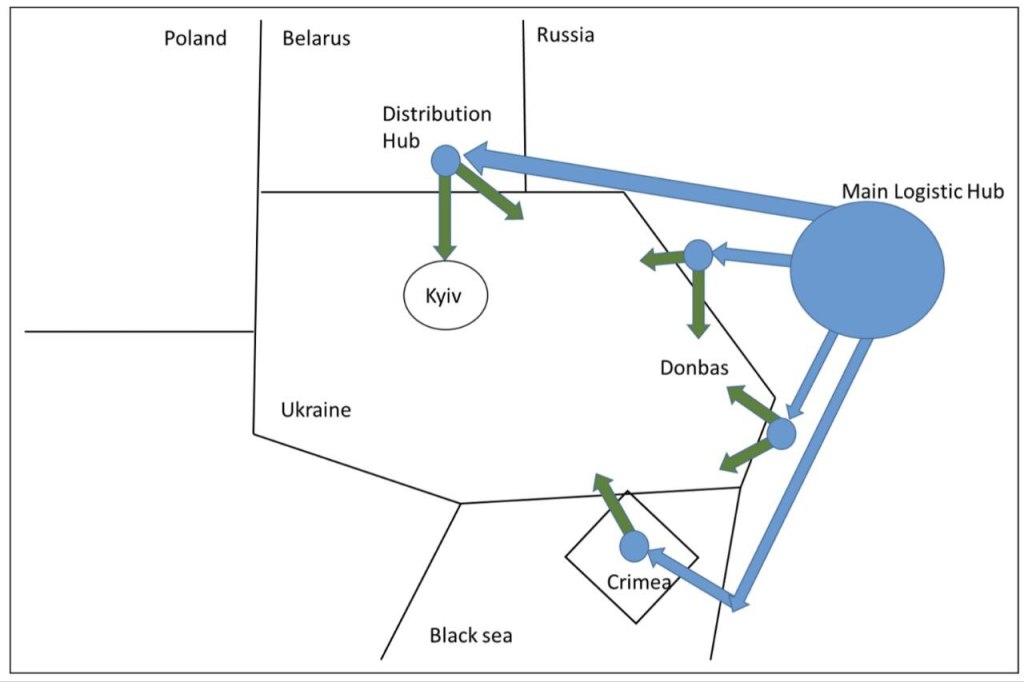
The Russian military exercises before the war with Ukraine included logistics planning for supply, maintenance, medical services, and transportation. The Zapad-2021 exercise had a detailed logistics plan, but it was unclear if it covered the war. Reports suggest the exercises were preparations for an invasion, and the invasion plan was likely known beforehand. However, logistics planning may not have been involved. The Russian logistical problems in the early phase of the war had a negative impact on their military capability. The initial logistics plan for the invasion involved locating supply hubs at strategic railway junctions and distributing supplies by trucks.
Main Reasons
Inadequate preparation
According to Per Skoglund, Russia’s military equipment was in poor condition even before the Ukraine war. The recent Zapad 2021 exercise conducted along the Ukrainian border with Belarus may have worsened the situation as units probably did not have enough time to maintain and service their equipment and vehicles, resulting in a “supply debt.”
Railroad-based Russian logistics
These findings are based on assumptions about Russia’s logistics, which rely heavily on transportation by rail. Due to successful attacks on rail connections by Ukraine, it became challenging for Russian logistics brigades to support their units. Researchers estimate that most ground transport in Mariupol was used to carry artillery ammunition due to the extensive shelling. This shortage of resources reduced the intensity of the battle, delayed movement of units, and continued to be a problem for Russian forces, according to Per Skoglund. When Russia succeeded in eastern Ukraine, they faced logistical challenges due to the distance from railway hubs.
Failed attempt to seize the airfield
The Russian forces had prepared for a brief invasion and equipped their troops accordingly, intending to capture the Antonov Airfield near Kiev to establish a logistics base. The failure to capture the airport left the units outside Kiev without adequate supplies, and although they had enough for five days, they managed to stay longer in the area. This shortage of supplies is likely the reason for looting and a lack of food, water, and equipment for the Russian soldiers, according to Per Skoglund.
Hierarchical command and control system
The command and control structure of the Armed Forces played a significant role in their inflexibility. For instance, the truck convoy that was stalled outside Kiev highlights the hierarchical command system’s impact on logistics.
“This became apparent when the truck convoy came to a halt outside Kiev. Not knowing what to do, they asked for direction from the General Staff, who decided that they were to give up and redirect resources. The situation was handled at the highest level which took time.”
Sources: Russian Logistics in the Ukrainian War: Can Operational Failures be Attributed to logistics? Scandinavian Journal of Military Studies; Authors: PER SKOGLUND, TORE LISTOU, THOMAS EKSTRÖM
Swedish Defence University – The role of logistics in Russia’s setback in Ukraine.
Russian Military Logistics Russia’s War in Ukraine Series No. 3, International Center for Defence and Security.; Author: Ronald Ti