Value Stream Mapping (VSM) is one of the fundamental tools of the Lean Manufacturing methodology. During the degree it is a tool that I was taught to use and that I consider very useful, and that is why in this post I will explain its importance and the basic steps to elaborate a VSM by yourselves.
What is a VSM and what is it for?
The main objective of VSM is to identify those activities that do not generate value in the production process and in the logistics management of a product. To do this, the different flows (information, work and movement) of the different activities and stages through which a product passes are analysed. This makes it easier to visualise where inefficiencies exist in the production process and to detect opportunities for improvement.
This tool has an impact on logistics, as it takes into account logistics operations such as the supply of raw materials, storage conditions or order distribution. Value stream mapping allows for a current analysis of logistics flows and the identification of cost overruns or time losses that can be solved by installing automated storage systems, deploying warehouse management software or implementing a new order picking method.
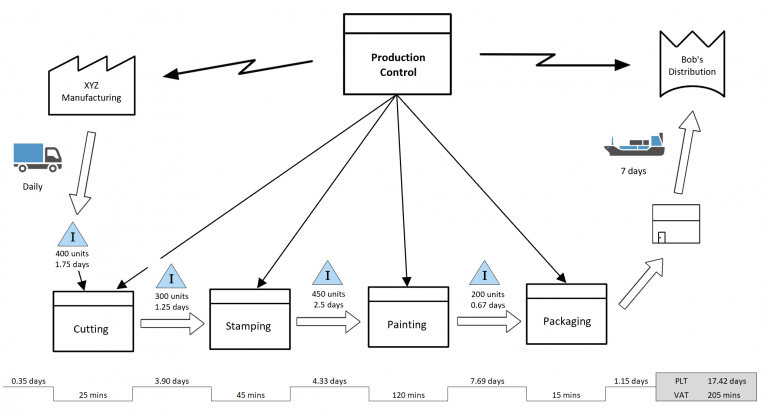
Steps to make a VSM
Implementing a Value Stream Map to optimise our production process involves following a series of steps. Below is a summary of the main steps to follow in order to have a general idea of how to do it.
1. Define the scope: Start by identifying the process or value stream you want to analyse. Define the scope of the VSM, whether it will be the entire process or a specific section.
2. Team: Form a multi-disciplinary team representing the different functions involved in the process. This will ensure a complete understanding of the whole process.
3. Current state VSM: Perform a comprehensive mapping of the current state of the process. It uses standard symbols to represent activities, inventories, lead times and information flows. In this step, data on cycle times and key performance metrics are collected.
4. Waste identification: Examine the map to identify activities that do not add value, such as waiting, unnecessary movements and overproduction. These should be highlighted and analysed in detail to see how to improve it.
5. VSM future state: Work with the team to design an ideal future state for the process. Eliminate the identified waste and implement the improvements proposed in the previous step.
6. Implementation plan: Defines a detailed implementation plan to realise the future state. Prioritise the identified improvements and set a clear timetable.
7. Validation and monitoring: implements the planned improvements and regularly monitors to assess their effectiveness. Measures and compares results with baseline data. Readjust if necessary.
Value Stream Mapping is a very powerful tool that allows us to understand and optimise our entire process. It allows us to visualise, analyse and improve the different stages of the production process of a product, from the reception of raw materials to production, storage and final delivery to the customer.
Here is a link to an online tool to make your own VSM: https://online.visual-paradigm.com/es/diagrams/features/value-stream-mapping-software/