
In this subject, we have talked a lot about how Supply & Logistics Management became a key component inside companies. With the development of communication, transportation systems, the demand is increasing and diversifying constantly. Highly developed logistics models have been developed, and now gigantic retailers like Amazon are able to fulfill a large part of the world on a wide range of objects.
However, we have mainly concentrated our thinking on goods and warehouses, but what about managing human lives? The number of disasters have been multiplied by 3 in the last 30 years (see graph n°1), but fortunately the number of death have decreased. This is all due to the development and installation of frameworks and actions in order to react in case of disaster : disaster management and logistics.
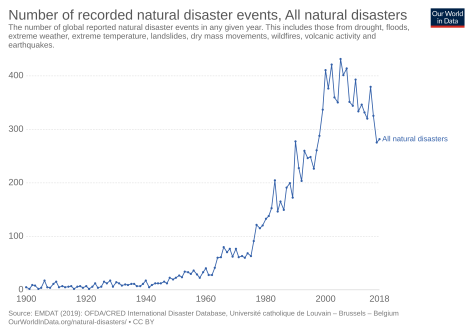
Table 1 : Number of recorder natural disaster events, all natural disasters
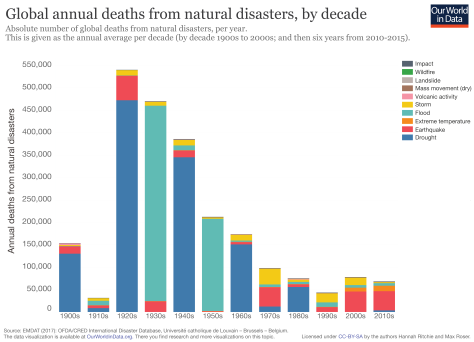
Table 2 : Number of Annual Deaths from natural disasters, by Decade.
A few statistics about Disasters
The development of natural disasters over the past decades can be in part explained by the important climate changes. According to this TEDx Video, between 1980 and 2009:
- The economic losses from natural disasters have more than tripled
- The number of natural disasters have doubled
- Low-Income and Middle-Income countries have lost 1.2 trillions due to damage (equivalent to 1/3 of the Developement Financial Help given on this period)
- 2.3 billion people have perished due to natural disaster
And as the population keep growing, especially in developing countries, the potential risks of losses is going to grow necessarily. Therefore, the need for a strong prevention and reaction policy is unavoidable.
The different types of Disasters
| Rapid onset natural disasters
Earthquake, Tornados, Storms… |
Slow onset natural disasters
Starvation, famine, epidemics |
| Rapid onset man-made disasters
Terror attacks, Industrial Accidents |
Slow onset man-made disasters
Economic crises, Refugee crises |
Those different type of disasters requires different type of prevention. However, the most difficult to prevent and avoid are Rapid onset natural disasters, such as the gigantic Tsunami of 2004, in Japan, that caused many deaths.
The stages of Disaster Logistics
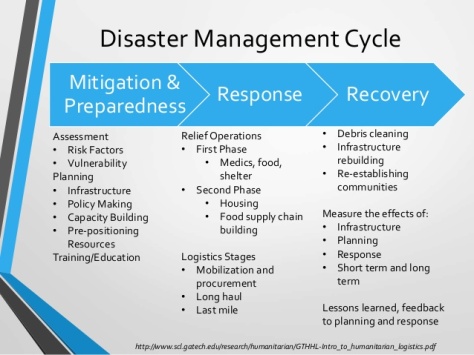
1. Preparedness Phase
The most important phase. But also the most forgotten one. In the previous TEDx video, we learn that in the $90 Billion that have been given by the international community for disaster-related assistance, only $3.25 Billion (3.6%) have been for prevention and preparedness.
In this phase, it is important to be able to assess and identify the different point of vulnerabilities in the area (fragile buildings, difficulties for evacuation, time for intervention…), but also to identify what would be the needs in case of disasters. Pre-positioning of aid materials (Food, Water, Medical help) is therefore fundamental : Docters without Borders and Red Cross have pre-positioned warehouses in critical areas. World Vision (https://www.wvi.org/) have also 44 000 employees over 100 world, to ensure the arrival of aid to children and communities in need.
2. Response Phase
This is the phase where logistics activities are the most used. The efficiency of this phase will depend on the quality of the work that have been done on the first phase : the right distribution of aid materials and sufficient aid personnel. Hence, rapiditity is very important at this stage.
3. Recovery Phase
The last and most difficult phase, which take the longest time. Buildings but also communities are being destroyed, and need support to be repaired : for example, after the 2004 Tsunami, humanitarian aid organizations gave boats to fishermen, in order to help them to recover the local economy.
On top of ensuring the reconstruction of buildings, aid organization must ensure the self sufficience for the victim : in the long term, not everyone is going to be able to adapt themselves to these post-disaster conditions.
Finally, a strong analysis of the damages and the execution of this disaster management have to be done, in order to extract information and prevent future cases of disaster.
Conclusion
Disaster logistics are more complicated than goods and warehousing, as they are being developed for one-time event, and therefore there is no possibility to simulate completely a disaster. However, it is possible to reduce the damages of those disaster by analyzing the biological reasons, to be able to prevent them and apply defined processes.