The Ongoing Convergence of Cloud and Logistics/Supply Chain Software
How Software-as-a-Service (Saas) took over the supply chain software market, where it stands now and how far we have to go before the supply chain is truly autonomous.
Coming into 2020, the worldwide public Cloud services market was on track to grow by 17% for a total of $266.4 billion in revenues this year—up from $227.8 billion last year. “At this point, Cloud adoption is mainstream,” Gartner’s Sid Nag pointed out at the time. “Adoption of next-generation solutions are almost always ‘Cloud-enhanced’ solutions, meaning they build on the strengths of a Cloud platform to deliver digital business capabilities.”
Breaking the Cloud down into two different segments, Gartner said software as a service (SaaS) will claim $116 billion of the market in 2020, while Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) will hit $50 billion. Gartner attributes much of the growth to the demands of modern applications and workloads, “which require infrastructure that traditional data centers cannot meet.”
Safe to say, COVID-19 will elevate those numbers even further as companies scramble to find technology that supports more remote, socially-distanced work arrangements. So, while Cloud adoption was already on the rise—with very few companies doing big, on-premise software installations anymore—it’s taking on a larger responsibility as organizations invest in applications that help them be more flexible, agile and resilient.
Supply chain software has been front-and-center in many of these conversations. Valued at over $15 billion, the supply chain management (SCM) sector grew at an 8.6% pace in 2019, exceeding $15 billion in vendor revenue by helping companies automate and manage their domestic and global supply networks.
According to Balaji Abbabatulla, Gartner senior director analyst of product management research for SCM software, Cloud software revenue grew almost 2-1/2 times faster than the overall SCM market in 2019. In total, it accounted for nearly 34% of the market as all leading vendors in the space took their new product strategies into the Cloud.
“The impact of Cloud has been all-pervasive across all of the supply chain submarket segments,” Abbabatulla points out. Gartner divides those segments into procurement, supply chain planning (SCP) and supply chain execution (SCE) applications. For procurement, he says many of the procurement platforms being adopted right now are Cloud-based, and many of their users are accessing those platforms remotely (via the Cloud). “It’s really about usage and adoption,” he says.
In the SCP space, Abbabatulla is seeing a big push for legacy software modernization that’s being supported by the adoption of Cloud-based applications. Much of what’s in place right now is antiquated, so companies are looking for new ways to be able to react quickly across multiple time horizons. Cloud is helping them achieve those goals, and more.
“At a broader level, business leaders are looking for tech tools that help them achieve better supply chain resilience—as opposed to finding ways to improve efficiency and productivity,” says Abbabatulla. “Where efficiency was once a driving force for Cloud-based SCP adoption, now it’s all about resilience.” Credit COVID-19 with driving this trend. Where Cloud was a “nice to have” pre-pandemic, it has since become a “must have.”
“COVID has made it imperative for supply chain leaders to have some form of a modern planning solution that cuts across various individual functions—be it sourcing planning, execution planning, manufacturing planning or sales and distribution planning,” Abbabatulla explains. “To manage any of these functions, organizations need to be able to understand and react quickly to environmental changes.” 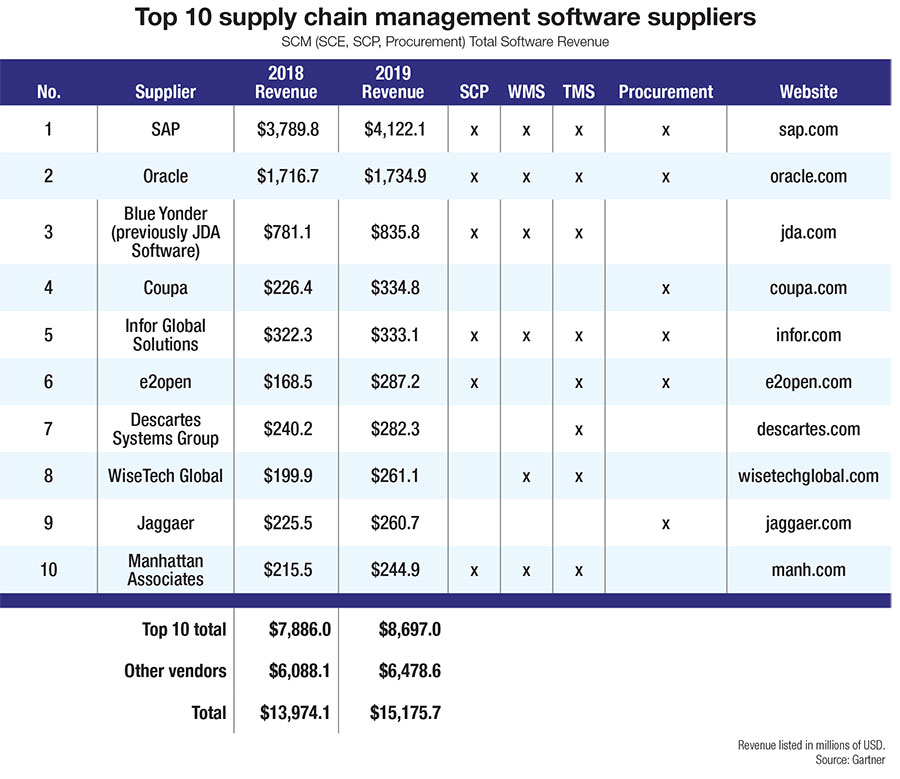
Improving productivity and efficiency
As the third component in Gartner’s 3-legged SCM stool, SCE is all about improving operational productivity and efficiency. It’s where warehouse management systems (WMS), transportation management systems (TMS), yard management systems (YMS) and others come together to support the overall supply chain. Using the warehouse as an example, Abbabatulla says Cloud-based WMS stands at the intersection of emerging technologies and the need for multi-enterprise collaboration.
“The Cloud allows warehouse applications to integrate with external sources that, in turn, send signals (i.e., a delay or disruption in the upstream supply chain) that help the company in question automatically optimize its own internal processes,” Abbabatulla explains. “As a result, overall internal efficiency improves.”
As Cloud continues to affect all three facets of SCM, Abbabatulla expects to see more companies moving over to this software delivery model. With or without technology, he says all organizations are focused on enabling better decisions by improving intelligence in the supply chain. A trend exacerbated by COVID-19, this movement in and of itself continues to drive the high demand for Cloud-based supply chain software.
Moving toward the autonomous supply chain
Operating in a world where the ability to make anything “autonomous” is technology’s latest siren call, supply chain managers are envisioning a day when some or all parts of their global supply chain are, indeed, autonomous. The Cloud could help them get there.
Salim Shaikh, a digital transformation executive at Blue Yonder, says the high levels of uncertainty that COVID-19 brought with it are driving even more supply chain operations to explore their autonomous supply chain options. Seeking better resilience and adaptability, more of these companies are looking to the Cloud for help in this area. For many, the “Holy Grail” is the autonomous supply chain, or that place where planners can use real-time data to reduce latency, manage disruption and turn their attention to more value-added tasks, like managing exceptions and collaborating with customers and suppliers (versus analyzing data).
For the company that doesn’t want to rip out and replace the on-premise systems that it has been using for decades, the Cloud paves the path to newer, more modern applications that can be integrated into existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) and other systems using application programming interfaces (APIs).
“This allows organizations to leverage new software capabilities and technology like machine learning, artificial intelligence (AI) and predictive/prescriptive analytics,” says Shaikh, “on top of their existing solutions.”
Acknowledging that the autonomous supply chain creates predefined scenarios that can be automatically implemented when a particular event is triggered, Abbabatulla says the end goal for such supply chains is that every single supply chain decision should be made and implemented autonomously. And while this is certainly something to aim for in the future, Abbabatulla says we’re not quite there yet, nor is it presently a key driver of Cloud-based SCM investment.
“The autonomous supply chain has long-term business potential,” Abbabatulla concludes, “with supply chain leaders currently investing in applications that improve their business outcomes today, so they can recover from the downturn, gain competitive advantage and grow quickly.”
The modernization of the supply chain
With all of the top supply chain software providers now offering Cloud-based options—and some focusing solely on this delivery model—it’s no longer a question of if a company is going to move in that direction, but when that’s going to happen. As chief sustainability officer and group vice president of SCM product strategy for Oracle, Jon Chorley says COVID-19 has brought to light the value of the Cloud across nearly all software segments, SCM included. For example, he says Cloud go-live implementations can take place 100% virtually, which means no worries about travel, social distancing or other COVID-related workplace challenges.
The fact that Cloud-based SCM integrates machine learning, AI, IoT and even blockchain (in some cases), makes it particularly attractive for newer companies, and for those that are saddled with on-premise and legacy systems that lack the modern bells and whistles. With little to no investment being funneled into non-Cloud-based enterprise software platforms at this point, Chorley says the “pendulum has swung” over to the SaaS delivery model.
“Companies are recognizing that some of these newer technology capabilities can really make a difference in supply chains,” he adds, “and they want to leverage them within their own environments.”
Where in the past these add-ons may have required expensive customizations, consulting and integration work, most are simply built into the modern, Cloud-based options. “As technology continues to evolve and develop, those capabilities just become part of our solution,” Chorley says. “You can’t go out and integrate them, extend your software or add them on. They’re part of the intrinsic value proposition.”
5-year success plan
Looking ahead, Abbabatulla sees three phases of supply chain modernization coming. The first is migration to the Cloud (timespan: 2021-2022); followed by process modernization supported by growth technologies such as AI and advanced analytics (2022 and beyond); and finally, we’ll see process augmentation, as companies will implement emerging technologies such as hyper-automation to deploy convergent SCM solutions across their global supply chains in 2023 and beyond.
By the time 2025 rolls around, more companies will have gone beyond just creating specific pockets of intelligence or resilience in their operations, and will be using technology to extend those strengths across the broader supply chain. “By phase three,” says Abbabatulla, “organizations will be getting true value from the investments they made during the first two phases

Article Topics
Software News & Resources
What generative AI means for supply chain work Reverse logistics in need of some love 2024 WMS Update: At the intersection of warehousing and e-commerce Vendor Evaluation Questionnaire for RFPs Supply Chain Management (SCM) applications keep the supply chain humming 6 TMS Trends for 2024 Getting ahead of the next supply and production disruption More SoftwareLatest in Logistics
FTR Shippers Conditions Index enters negative territory DAT March Truckload Volume Index sees modest March gains National diesel average, for week of April 22, is down for the second straight week UPS reports first quarter earnings declines LM Podcast Series: Assessing the freight transportation and logistics markets with Tom Nightingale, AFS Logistics Investor expectations continue to influence supply chain decision-making The Next Big Steps in Supply Chain Digitalization More LogisticsAbout the Author
Subscribe to Logistics Management Magazine

Find out what the world's most innovative companies are doing to improve productivity in their plants and distribution centers.
Start your FREE subscription today.
April 2023 Logistics Management

Latest Resources
















